Care and Handling of Instruments/Sets
Perioperative nurses work in conjunction with Medical Device Reprocessing staff to create and update surgical instrument sets. Many hospitals have implemented instrument inventory management systems that are excellent for productivity, inventory management and staff educational purposes.

Benefits of Inventory management systems
Inventory Management Systems:
- assist with the composition of instrument sets
- provide screen-based set lists, photos of instruments, tray assembly and processing
- track individual instruments
- track the number of usages
- track the individual instrument’s repair history
- track the total instrument inventory
- track the maintenance schedule
Watch this quick video to see an example of an instrument management system:
Designing an Instrument Set
Considerations for designing an instrument set include:
- The surgical procedure being performed
- The frequency of set use
- Accurate numbers of each instrument type
- Maximum weight of the instruments combined with the container (10kg)
- The surgeon’s preference
- The population (i.e. pediatric or bariatric)
- Instrument types (all need to be sterilized in the same manner)
- The table set up
When preparing surgical sets, a standardized list is used of all types and numbers of required instruments based on the surgical requirements. Uniformity of sets helps with inventory management, predictability in the operating room, and facility of surgical counts. (ORNAC. 2021).
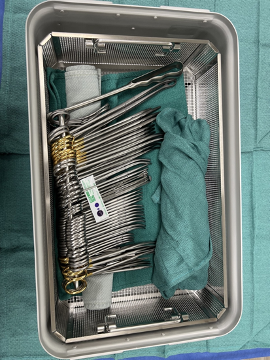
Instrument sets are specifically configured to:
- minimize damage to delicate instruments by placing all heavy items such as retractors on the bottom of the tray with delicate instruments on top, and using tip protectors on sharp tips
- maximize efficiency for surgical set up by stringing clamps and placing like instruments together

Rigid Containers
Types of rigid containers used to sterilize instruments are dependent on:
- manufacturer recommendations for the instrumentation
- sterilization modality
- institutional reprocessing policies and procedures
- safety concerns – the combined weight of the container and instruments should not exceed 10 kg (22 lbs)
(Canadian Standards Association, 2010).
Building the Case Cart
Each surgeon will have a “pick list” which may be called various names depending on your facility. This list is a recipe card for the specific surgical procedure. It lets MDRD (Medical Device Reprocessing Department) and the perioperative nurses know which supplies the surgeon usually uses for a specific case. Based on this list, MDRD will select the instrument sets and individually wrapped, reusable or disposable supplies. These will be added to a case cart. Once the supplies have been placed in the cart, it is sent to a clean designated area near the OR. This is where the perioperative nurses make sure all supplies are present before bringing the cart into the room and setting it up for the procedure.
Intraoperative Instrument Care
It is important to:
- Protect delicate items. Place them separately on the setup. Do not place heavy instruments where they may be crushed.
- Pass instruments with care, Ensure they are passed back after use to prevent damage while on the sterile field or by falling onto the floor.
- Use sterile water and cloth to wipe bioburden off.
- Instruments during surgery because normal saline can cause pitting of instruments.
- Flush cannulated instruments such as suction and irrigating tips with water-filled syringes to clean during surgery. (Cromb, 2019)
End of case
It is important to:
- Place instruments back in the set in the original format – i.e., heavy items on the bottom with delicate separate. Transport instruments to the MDRD for immediate decontamination as bioburden increases on contaminated instruments that are left to dry.
- Use enzymatic detergent sprays or solutions to treat instruments immediately postoperatively if unable to decontaminate right away. Enzymatic removes and breaks down organic soil reducing bioburden, particularly in hard-to-reach areas.
- Keep instruments moist to prevent drying and make for easier cleaning.
(MDRAO, 2018)
Summary
Nursing knowledge of evidence-based practice guidelines for instrumentation is critical for safe, efficient care. Perioperative nurses sometimes act as consultants for manufacturing companies by participating in trials of new instruments and equipment and providing professional feedback. Nurses may also participate in the fiscal responsibility of purchasing and inventory control by sitting on hospital committees.